The World’s Deadliest Food: Cassava and Its Deadly Potential for 500 Million People
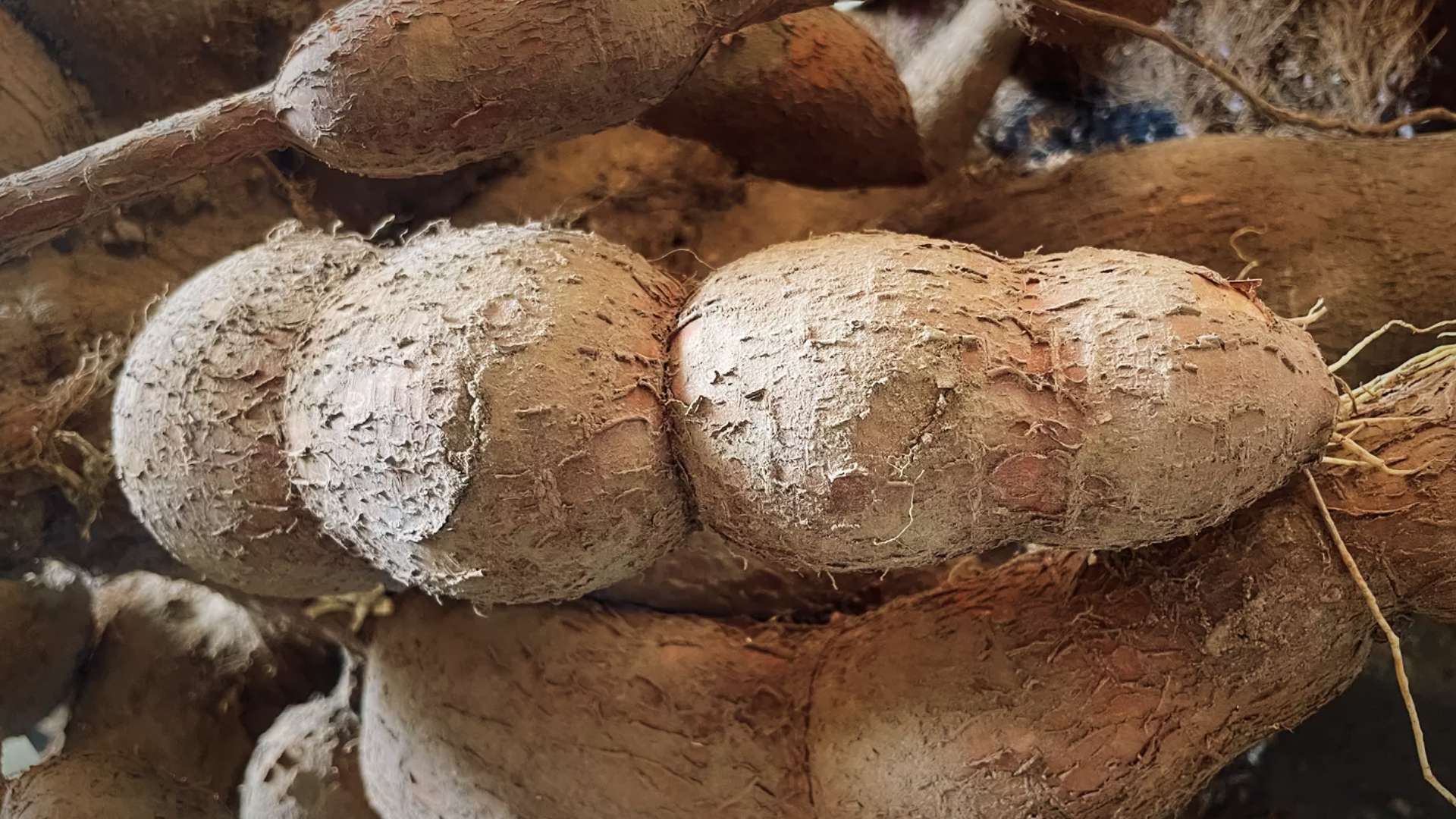

Cassava, a tropical root vegetable, is known for being one of the deadliest foods in the world, despite its widespread popularity. Around 500 million people consume cassava regularly, and yet, this seemingly innocent food hides a deadly potential if not prepared properly. Though many cultures rely on cassava as a vital source of sustenance, its toxic nature remains a concern.
Let’s take a closer look at this fascinating food, its risks, and how millions have learned to enjoy it safely. But first, why is cassava so deadly, and why does it still remain a part of everyday diets across the world?
What Is Cassava, and Why Is It So Dangerous?
Cassava, also called manioc or yuca, is a starchy root vegetable native to South America. It thrives in tropical climates and is one of the top staple foods in countries like Nigeria, which is now the world’s largest producer of cassava. It is grown in more than 100 countries and plays a central role in food security for millions, especially in parts of Africa, Asia, and Latin America.
While cassava is a crucial food crop, its danger lies in the toxic substances found within the plant. The root, peel, and leaves of cassava contain cyanogenic glycosides. These compounds can release hydrogen cyanide, a deadly poison, when the plant parts are not properly prepared before consumption. Even small amounts of cyanide can cause serious poisoning, which is why preparation is key. Source on Cyanide Poisoning.
Interestingly, sweet varieties of cassava contain lower levels of cyanide compared to the bitter types, but even the sweeter varieties can be dangerous if consumed without proper processing. While cassava is a nutritious food source, these potential dangers make it a food that demands respect and careful handling.

Why Does Cassava Have Such a Deadly Reputation?
Cyanide poisoning from cassava is responsible for an estimated 200 deaths annually, according to the World Health Organization (WHO). Though it may sound alarming, millions of people eat cassava without ill effects. The key lies in preparation and processing methods. When the cassava is properly prepared, the risks are significantly minimized.
Many communities around the world have passed down generations of knowledge on how to safely prepare cassava. For instance, soaking the root for 24 hours before cooking helps to reduce the cyanide content, and in some places, people use fermentation techniques to further lower the risk. Cooking methods such as boiling or frying also help eliminate toxins. This process of preparation is crucial in ensuring that cassava remains a safe and nutritious food. Health Risks of Cassava.
However, things go wrong when these safety measures aren’t followed. The risks increase when people consume raw or inadequately prepared cassava, which has been linked to severe health issues such as a neurological disorder called ataxia. Ataxia can cause symptoms such as uncoordinated movement, balance issues, and, in severe cases, paralysis or death. The effects of cyanide poisoning are not immediate, but when left unchecked, they can cause long-term damage to the body. Learn More About Ataxia.
How Cassava Is Prepared Safely
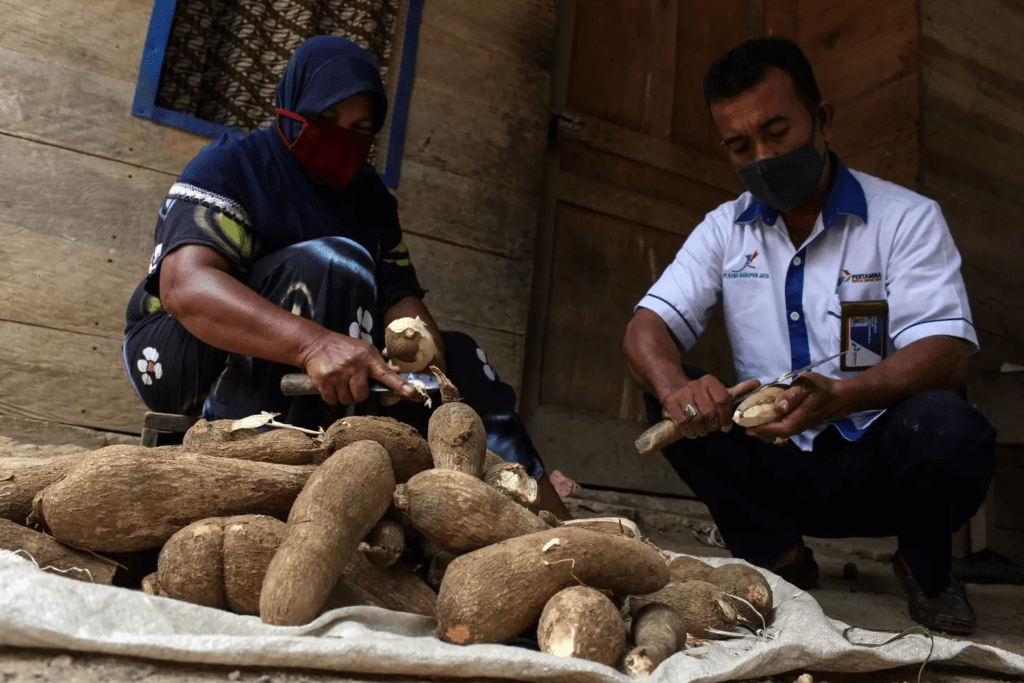
One of the most common methods for making cassava safe to eat involves soaking the root for up to 24 hours to help eliminate toxins. In some regions, people also use fermentation techniques or boil the roots for several hours. These methods significantly reduce the cyanide levels and make the root edible without the risk of poisoning.

It is essential to note that the leaves and peel of cassava should not be eaten raw at any cost, as they contain higher concentrations of cyanogenic compounds. Even the more harmless parts of the plant, such as the root, must undergo proper preparation before they can be consumed. Additionally, some cultures even dry the cassava and grind it into flour to further detoxify the plant, making it safer to consume. How to Cook Cassava Safely.
Proper preparation ensures that cassava becomes a safe food item, though it’s crucial for those unfamiliar with its risks to take extreme care. Most cases of poisoning occur when these preparation guidelines are not followed, underscoring the importance of education on food safety practices, especially in areas where cassava is consumed regularly.
The Role of Cassava During Food Shortages
The danger of cassava is most pronounced during times of food insecurity or famine. When food supplies run low, people are more likely to turn to bitter varieties of cassava, which contain higher levels of cyanide. During the Venezuelan food shortages of 2017, for example, many individuals died after consuming bitter cassava without properly processing it.
While cassava has historically been a lifeline for many communities during times of scarcity, its deadly potential is heightened when people are desperate and unaware of proper preparation techniques. People may turn to bitter cassava to stave off hunger, but consuming it raw or insufficiently processed leads to tragic outcomes. Ensuring that proper food safety measures are followed is crucial during periods of famine or food shortages. Food Security and the Risk of Cassava.
The relationship between cassava and food shortages is complex. On one hand, cassava’s resilience and ability to grow in poor soil conditions make it an important crop in areas with limited access to other food sources. However, its deadly potential when not properly handled can turn it from a life-saving food into a silent killer during times of desperation.
Is Cassava Worth the Risk?
Despite its potentially deadly effects, cassava remains a crucial food for millions of people around the world. Its resilience and ability to grow in poor soil conditions make it an invaluable food source, especially in areas affected by climate change or unstable agricultural systems.
For many communities, cassava represents a critical part of their food security strategy. It provides a reliable source of carbohydrates and energy, particularly in regions where other crops struggle to grow. But this doesn’t mean cassava is a “dangerous” food per se—it’s all about preparation. When done right, cassava provides essential nutrients that help to sustain millions of people.

Though cassava’s potential for harm is real, its benefits cannot be dismissed. In fact, for many people, cassava is not just a food source; it’s a cornerstone of their daily lives. Educating people on the proper ways to prepare cassava can help reduce the risks and make it a safer food for everyone. More About Safe Food Preparation.
Preparing for the Worst: Cassava and Global Health
While most people who consume cassava do so without experiencing any negative health effects, it’s important to remain vigilant about food safety practices, particularly when dealing with foods that have toxic properties. Efforts to educate communities, improve agricultural techniques, and spread awareness about safe cassava preparation are key in preventing deaths related to cyanide poisoning.
In countries where cassava is a staple food, governments and organizations like the World Health Organization have made strides to educate the population about proper preparation methods. Awareness campaigns, research into safer cassava varieties, and the promotion of better food security practices are essential to reducing the risks associated with cassava. With improved practices, cassava can continue to provide food security for millions without posing unnecessary dangers.
The global health community has recognized cassava’s dual nature and has worked toward creating solutions that help people consume it safely. From creating new varieties of cassava that contain lower levels of cyanide to promoting safer cooking techniques, there are many ways to mitigate the risks and make cassava a safe food. More About Food Safety.
Final Thoughts: The Balance Between Risk and Reward
Cassava’s dual nature—life-giving when prepared correctly but deadly if mishandled—makes it one of the most fascinating and controversial foods in the world. Despite the risks, it continues to be a food staple for millions, and when prepared properly, it provides nourishment and sustenance.
Next time you see cassava on the menu, you’ll have a better understanding of the care required to make it safe. For those who live in regions where cassava is a major food source, the lesson is clear: proper preparation is not just a culinary choice, but a matter of life and death. While it is possible to safely enjoy cassava, the importance of following the correct procedures cannot be overstated.
If you’re interested in learning more about food safety and how to handle potentially dangerous foods like cassava, visit Food Safety and Preparation Guidelines.
Engage with Us!
Have you ever eaten cassava or come across other dangerous foods that we eat without realizing their risks? Share your experiences and thoughts with us on Social Media. Don’t forget to spread awareness on food safety—knowledge can save lives!
Featured Image Credit: Getty Stock Photo