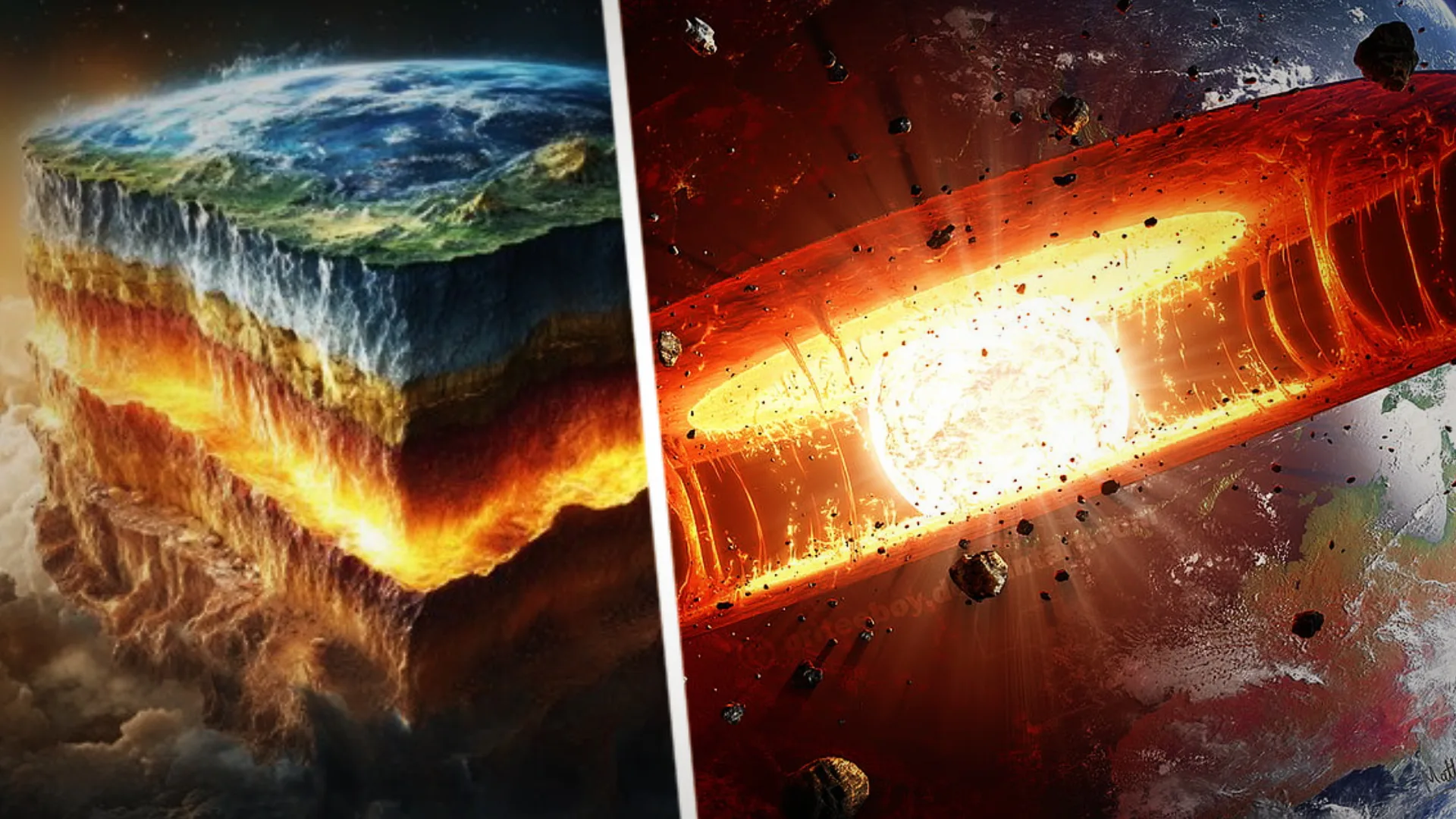
Scientists Uncover Shocking Truth About Earth’s Core—And It Could Impact the Length of a Day

A Groundbreaking Discovery That Challenges Everything We Thought We Knew
For decades, scientists believed that Earth’s inner core was a perfectly solid sphere, sitting deep beneath our feet and playing a crucial role in maintaining our planet’s magnetic field. However, a new accidental discovery made by researchers at the University of Southern California (USC) could change our entire understanding of the Earth’s core.
In a study that was initially aimed at something entirely different, scientists have found evidence that the inner core may not be as solid as we once thought. Instead, new seismic data suggests that it could be much more malleable, behaving in ways we never imagined.
This discovery, published in the prestigious journal Nature Geoscience, could even have implications for the length of a day on Earth—a revelation that might redefine how we perceive time itself.
What Exactly Did Scientists Discover?
Before diving into the specifics, let’s break down what we already knew about the Earth’s core:
- The Earth’s core consists of two layers—a liquid outer core and a solid inner core.
- It sits nearly 3,000 to 4,000 miles beneath the Earth’s surface and is made primarily of iron and nickel.
- The core is believed to be around 9% hotter than the surface of the Sun, reaching temperatures of about 9,800°F (5,400°C).
- It plays a vital role in generating Earth’s magnetic field, which protects us from harmful solar radiation.
Until now, scientists widely accepted that the inner core was a perfectly solid ball of iron. But according to the latest findings from USC researchers, this assumption might be wrong.
🌍🔥 Trending on Social Media: The Core Discovery Everyone’s Talking About
The internet is buzzing with reactions to this groundbreaking discovery! Scientists, science enthusiasts, and everyday people are sharing their thoughts on how the Earth’s core could actually be changing the length of a day.
Want to join the conversation? Check out these viral posts:
📢 Twitter/X:
“Wait… so the Earth’s core might not be solid after all? And it could be shifting our days?? Mind = blown. 🔥🌍 Read more #EarthCore #ScienceShocker”
📸 Instagram:
“New research suggests the Earth’s core may be more fluid than solid—could this mean our days are changing in length? What do YOU think? ⏳🌍 Check it out #BreakingScience”
📺 YouTube:
Watch USC scientists explain this shocking core discovery in detail: Click here 🎥🔥
💬 Reddit Discussion:
Curious about how this affects Earth’s rotation? Join the discussion on r/science: Join Here
What are your thoughts? Let us know in the comments below or tag us in your posts!
The Accidental Breakthrough: The Inner Core May Be More Fluid Than We Thought
John Vidale, a Professor of Earth Sciences at USC’s Dornsife College of Letters, Arts, and Sciences, led the research team that made this startling discovery. However, he admits that they weren’t even looking for it at first.
“We didn’t set out to define the physical nature of the inner core,” Vidale explained. “What we ended up discovering is evidence that the near surface of Earth’s inner core undergoes structural change.”
What Does This Mean?
This unexpected change in the inner core’s structure suggests that it may be shifting and deforming over time, a process known as viscous deformation. If this is true, it could mean that the length of a day on Earth is not as constant as we once believed—it may be changing due to subtle shifts in the core.
How Did Scientists Make This Discovery?
To reach this conclusion, Vidale’s team analyzed data from 121 repeating earthquakes occurring at 42 locations near the South Sandwich Islands in Antarctica.
By examining these quakes, researchers noticed something unexpected—certain seismic waves were behaving differently than anticipated, suggesting that the core wasn’t as rigid as previously assumed.
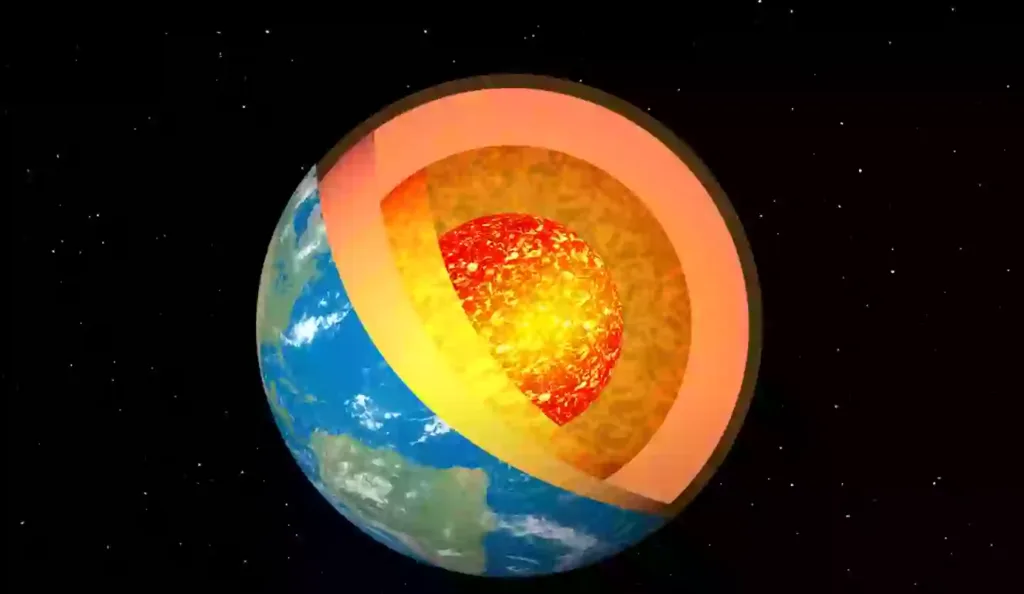
A Moving Core? The Role of the Outer Core’s Turbulence
One of the most fascinating aspects of this discovery is the interaction between the molten outer core and the solid inner core. Scientists have long known that the outer core is turbulent, but they never expected it to disturb the inner core within a human timescale.
Vidale elaborated on this, saying:
“The molten outer core is widely known to be turbulent, but its turbulence had not been observed to disrupt its neighbor, the inner core, on a human timescale. What we’re observing in this study for the first time is likely the outer core disturbing the inner core.”
Why Is This Important?
If the inner core is more fluid than we thought, it could be undergoing continuous changes, affecting how the entire Earth system functions. This might have long-term effects on Earth’s rotation and, consequently, the length of a day.
How Could This Discovery Impact the Length of a Day?
One of the biggest implications of this finding is the potential impact on Earth’s rotation speed. While the change would likely be imperceptible to humans, even tiny shifts in the core can gradually influence:
- The length of a day – Scientists already know that Earth’s rotation fluctuates slightly over time due to various factors, including glacial movements, atmospheric changes, and shifts in the mantle. If the inner core is deforming and interacting with the turbulent outer core, it could contribute to even more subtle variations in how fast the Earth spins. Over long periods, this might require adjustments in timekeeping systems like leap seconds, which help synchronize atomic clocks with Earth’s actual rotation.
- Our understanding of timekeeping – Atomic clocks help keep track of the most precise time on Earth, but if the planet’s rotation changes even slightly, we may eventually have to redefine how we measure time on a larger scale. These small but cumulative shifts could affect everything from GPS systems to satellite communications, which rely on precise time measurements to function correctly.
- Future geophysical models – If the inner core is more fluid than solid, researchers will need to rethink how they model Earth’s structure and its evolution over billions of years. This could impact predictions about future climate patterns, earthquake activity, and planetary stability in ways that are still not fully understood.
While this discovery raises many new questions, one thing is clear—Earth is not as stable and unchanging as we once believed, and our ability to measure time and understand planetary movements is evolving with every new breakthrough in science.
Rewriting the Textbooks: What Comes Next?
The new findings challenge long-standing assumptions about the inner core’s state, prompting scientists to revisit and refine their models of Earth’s interior.
Moving forward, researchers will likely conduct further seismic studies, using:
✅ Advanced earthquake data from around the world
✅ Computer simulations to model the inner core’s behavior
✅ Laboratory experiments replicating core conditions
As more data becomes available, we may soon have an even clearer picture of what lies beneath our feet—and whether our days on Earth might be subtly shifting in length.
Final Thoughts: Why This Discovery Matters to You
You might be wondering, “Why should I care about the Earth’s core?” The reality is that our planet is an interconnected system, and changes in one area can have ripple effects across the entire globe.
While this discovery won’t immediately impact our daily lives, it highlights how much we still don’t know about our own planet. Understanding the Earth’s core is crucial for:
🌍 Predicting natural disasters like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions
🧲 Studying the magnetic field that shields us from harmful solar radiation
⏳ Tracking time more accurately as the Earth’s rotation subtly changes
With future research, scientists may uncover even more surprises hidden beneath the Earth’s surface, reshaping how we understand our planet.
Want to Dive Deeper?
- Read the full research paper in Nature Geoscience
- Watch USC’s official explanation on YouTube
- Explore more about Earth’s core dynamics in NASA’s Earth Observatory
Featured Image Credit: Getty Stock Images