NASA’s Perseverance Rover Makes Mysterious Discovery on Mars!

Despite being Earth’s closest planetary neighbor, Mars remains a land of intriguing mysteries that space agencies, including NASA, are eager to unravel. While humanity has never set foot on the Red Planet, that might change soon, especially with SpaceX and Elon Musk’s ambitious plans to make Mars exploration a reality. For now, however, NASA’s Mars Perseverance rover continues to explore and analyze the Martian surface, shedding light on its many secrets.
The Discovery at Broom Point
For the past two weeks, Perseverance has been working at a location known as Broom Point, situated on the lower slopes of Witch Hazel Hill. This area lies on the rim of Jezero Crater, a large, ancient crater believed to have once been filled with water. The rover’s discovery at this site has left scientists intrigued a strange, spherical rock unlike any seen before. The rock, named “St. Pauls Bay,” consists of hundreds of small, dark grey spheres, some of which are elliptical, while others have angular edges, indicating they may be fragments of broken spheres. Some of these spheres also display tiny pinholes, adding to the mystery.
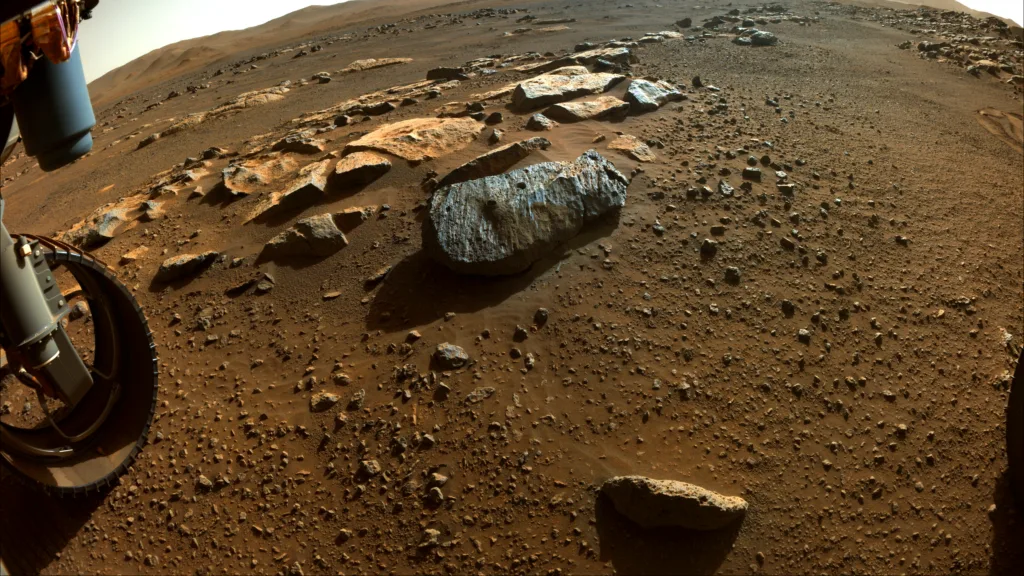

The Puzzle of Martian Spheres
This unusual find isn’t entirely new in the study of Mars. NASA first encountered similar spheres, often referred to as “Martian Blueberries,” in 2004, when the Mars Exploration NASA Rover Opportunity discovered them at Meridiani Planum. Since then, smaller spherical formations, known as spherules, have been found in other locations such as Gale Crater and the Neretva Vallis inlet channel in Jezero Crater.
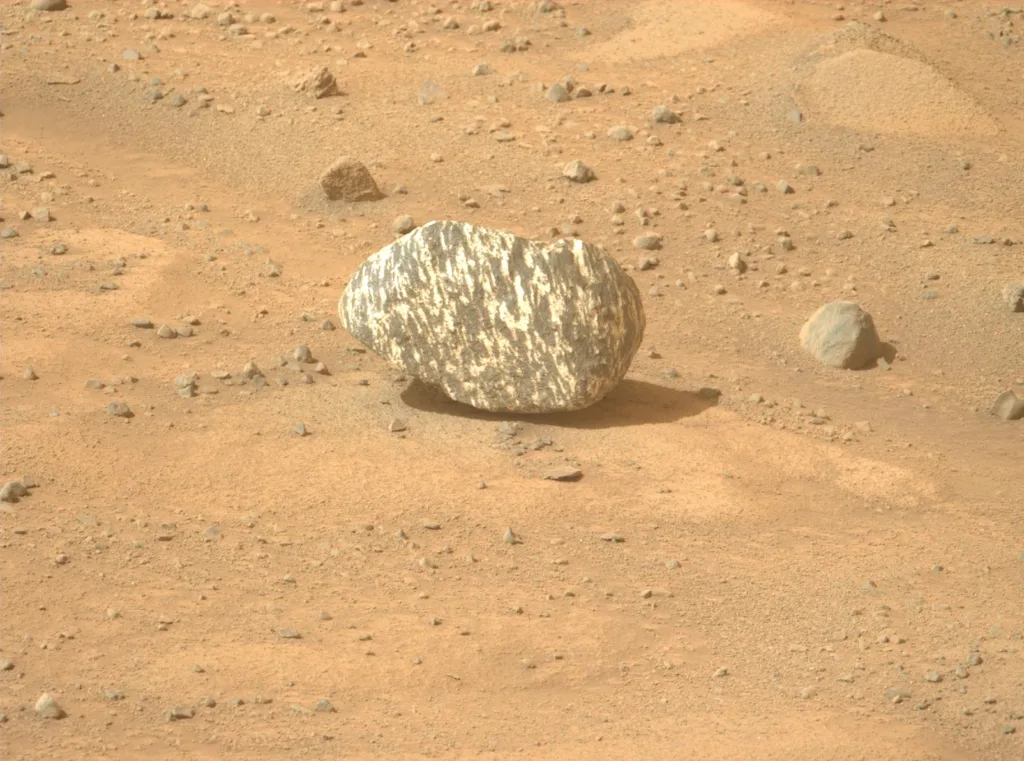

Scientists believe these spherules form through interactions with groundwater circulating through rock pores, a process that also occurs on Earth. However, not all spherules are created this way. Some can form during volcanic eruptions or even from the rapid cooling of molten rock droplets created by meteorite impacts.
A New Kind of Rock: ‘Float Rock’
What sets this discovery apart from previous ones is that these spheres appear to be a form of “float rock,” a term used by geologists to describe rocks that aren’t anchored to the ground. This feature, along with the unique appearance of the spheres, has left researchers puzzled, as they continue to investigate what specific geological processes could have produced these odd formations.

Continued Exploration of Mars
NASA’s Perseverance rover continues to serve as a valuable tool in the search for answers on Mars. While this latest find adds to the growing body of knowledge about the Red Planet, many questions remain. As the rover continues to analyze the Martian surface, scientists remain hopeful that they will uncover more clues about Mars’ past and its potential for harboring life.