“Google’s Quantum Breakthrough: Could Willow Chip Prove the Multiverse?”

Google’s quantum computing team has claimed a groundbreaking achievement that hints at a possible connection between their technology and the multiverse theory. Their new quantum chip, called Willow, has achieved computational speeds that surpass conventional understanding of processing power, suggesting it may operate in ways linked to parallel universes.
What is Willow?
Willow is Google’s latest quantum computing chip, designed to reduce errors and improve the efficiency of quantum computations. Quantum computers, unlike traditional machines, use qubits (quantum bits) that can exist in multiple states simultaneously, enabling them to perform highly complex calculations.
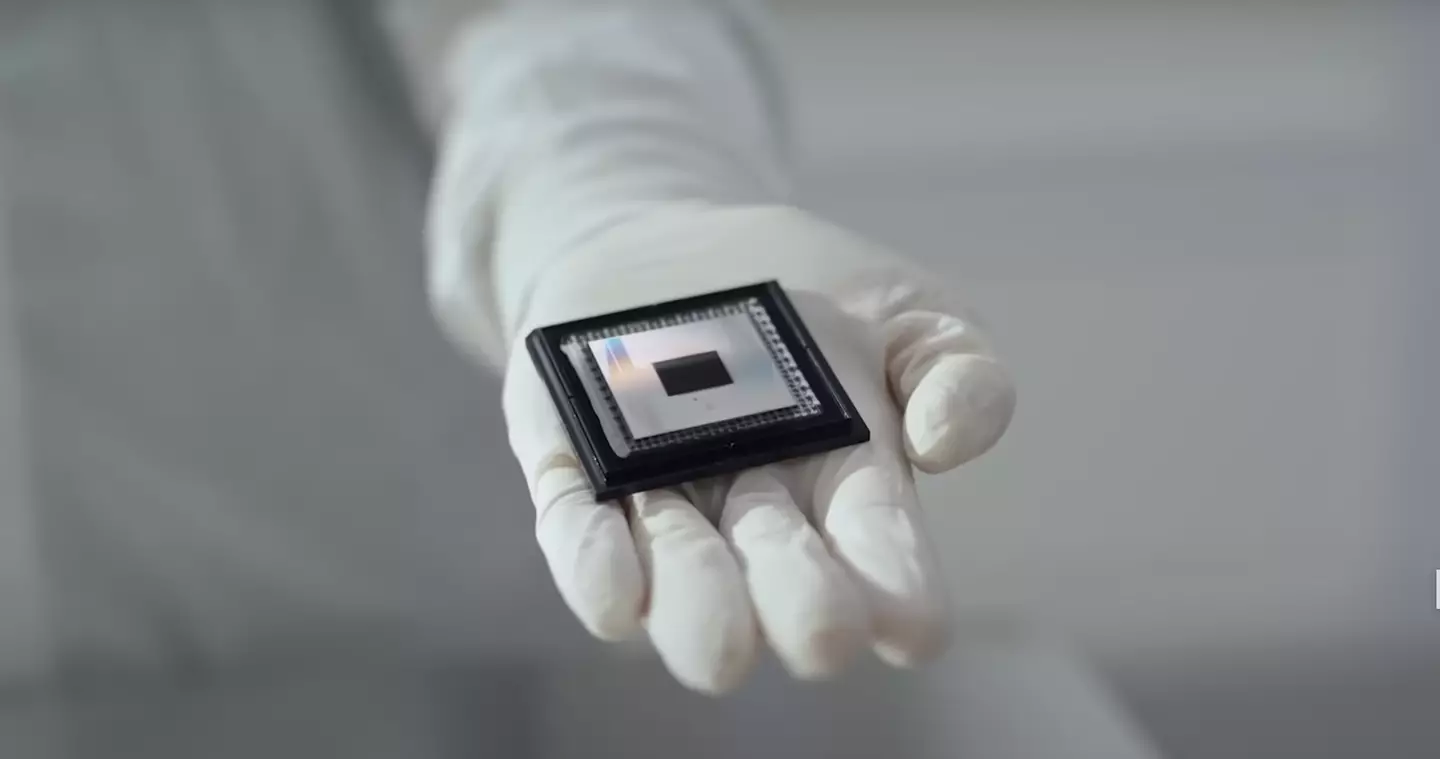
Willow is a new quantum computing chip from Google (Google)
- Willow’s feat: The chip completed a computation in less than five minutes that would take the fastest classical supercomputer an estimated 10 septillion years—a time scale far beyond the age of the universe.
- Error correction: Willow reduces computational errors by leveraging more advanced qubit designs.
The Multiverse Connection
Dr. Hartmut Neven, the founder and lead of Google Quantum AI, suggested that the astonishing performance of Willow might stem from its ability to access parallel universes. This concept aligns with the many-worlds interpretation of quantum mechanics, first proposed by physicist Hugh Everett and later expanded by David Deutsch.
- Parallel universes in action: Neven hypothesized that Willow could solve problems by drawing computational resources from multiple universes simultaneously, enabling speeds unattainable in a single physical reality.
- Theoretical foundation: Deutsch, an Oxford physicist and quantum pioneer, proposed in the 1990s that quantum computing’s power might be evidence of a multiverse, where computations happen across parallel realities.
Some people have cast doubts, however (Google)
Skepticism and Challenges
While the implications of Willow’s performance are awe-inspiring, critics remain cautious:
- Benchmarks: Doubters point out that Google’s claims are based on internal benchmarks, which may not reflect practical applications.
- Proof of multiverse: Critics argue that extraordinary computational efficiency doesn’t definitively prove the existence of parallel universes. Other explanations, such as advancements in quantum algorithms, could account for Willow’s speed.
What Does This Mean for the Multiverse Theory?
If Willow’s performance indeed involves accessing parallel universes, it could provide indirect evidence for the multiverse:
- Revolutionary physics: It would fundamentally reshape our understanding of reality, supporting the idea that we inhabit one of countless universes.
- Quantum supremacy: Google’s advancements might mark a new era where quantum computers transcend traditional limitations.
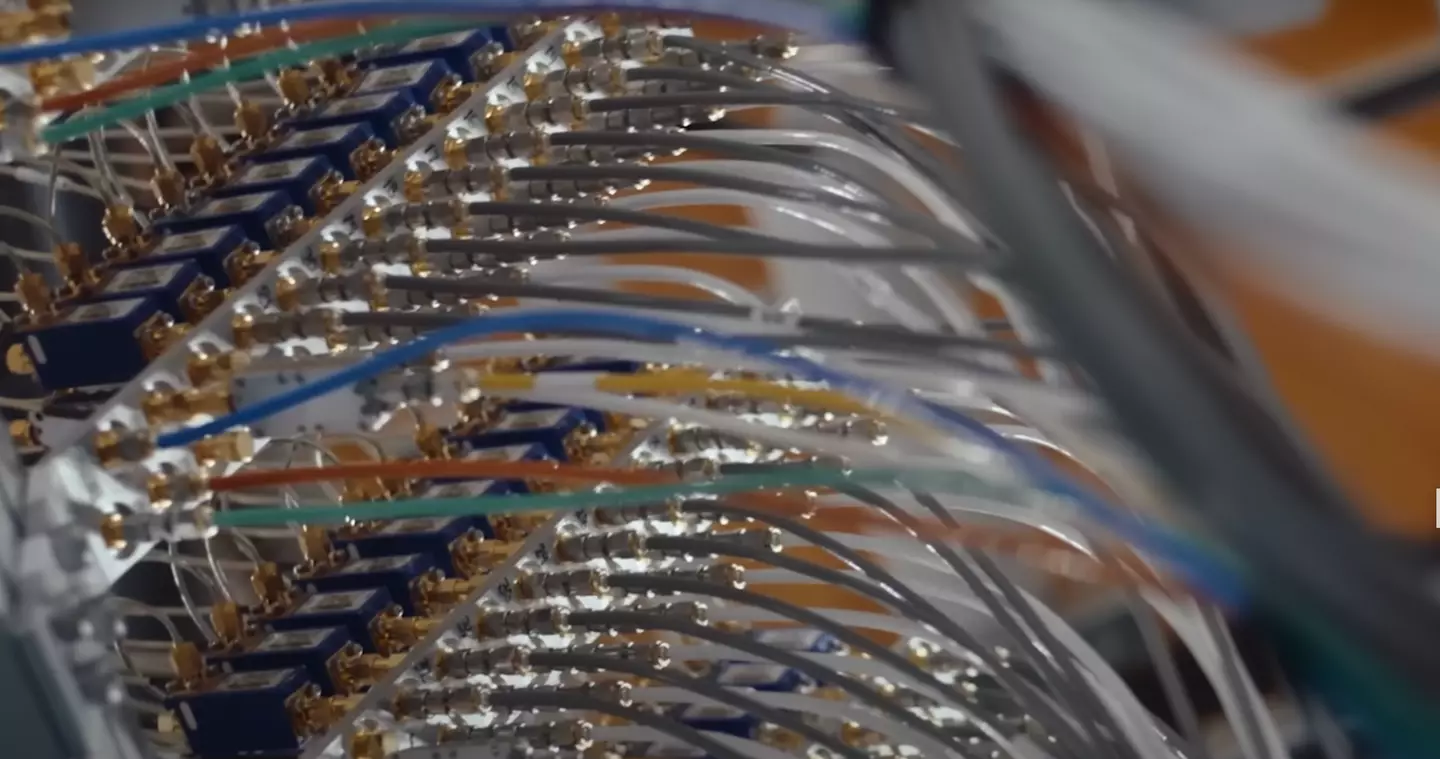
Apparently, all these wires help to draw information from parallel universes (Google)
Published Findings
The research, published in the journal Nature, provides technical details about Willow’s architecture and benchmarks. These findings are expected to spark further exploration into the intersection of quantum computing and theoretical physics.
What’s Next?
While the connection to the multiverse remains speculative, Willow’s unprecedented computational power could lead to breakthroughs in science, cryptography, AI, and other fields. As quantum computing evolves, it may bring us closer to understanding the true nature of our universe—or universes.
Featured Image Credit: Google






