A ‘Dent’ in Earth’s Magnetic Field Could Risk Our Way of Life
NASA Scientists on Alert
NASA scientists are on high alert after a troubling discovery in Earth’s magnetic field. This anomaly, referred to as the South Atlantic Anomaly (SAA), could pose serious risks to our technology, health, and even our ability to function as we know it. While this region of space may seem distant, its implications are very real and immediate.
What is the South Atlantic Anomaly?
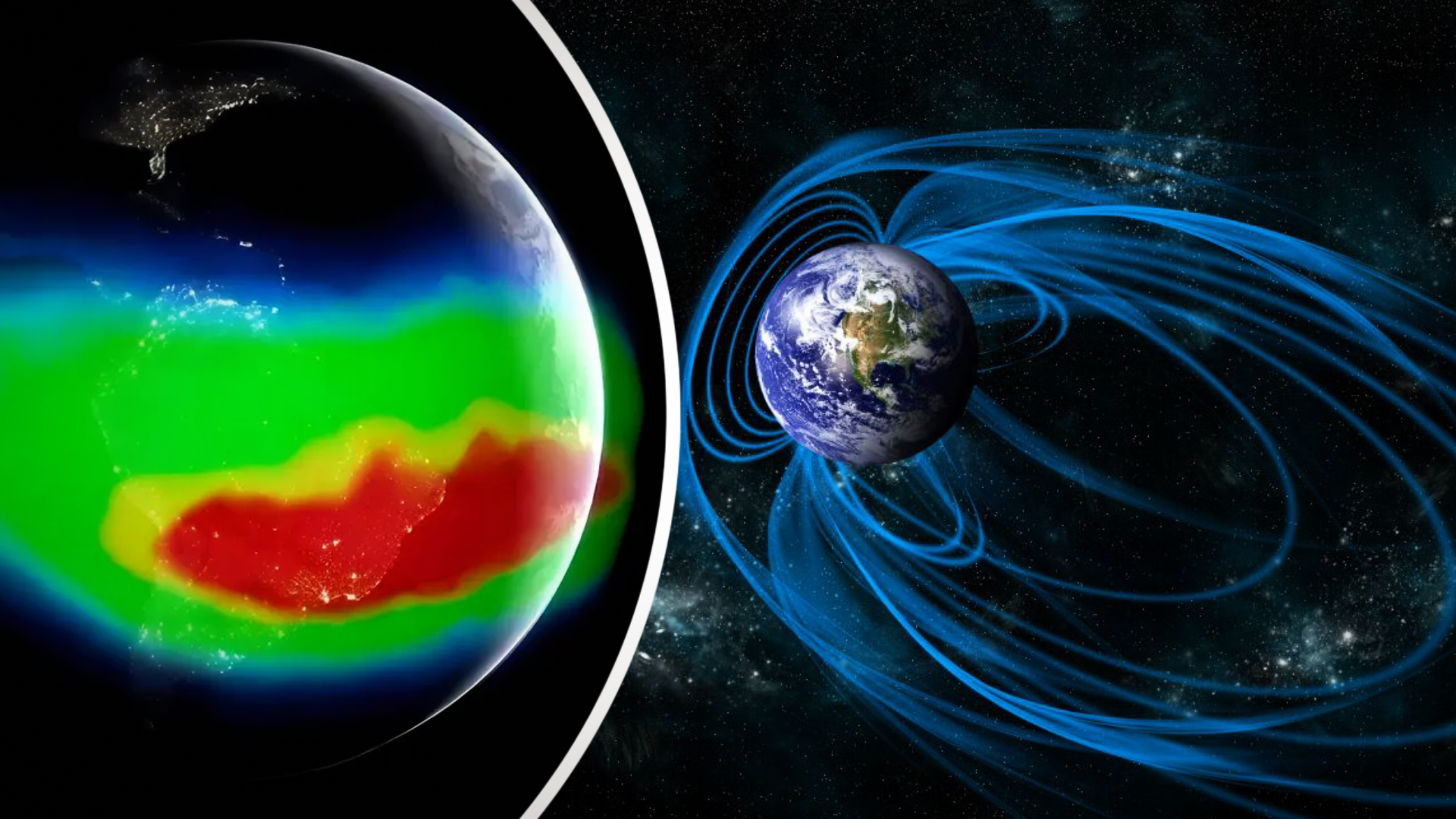
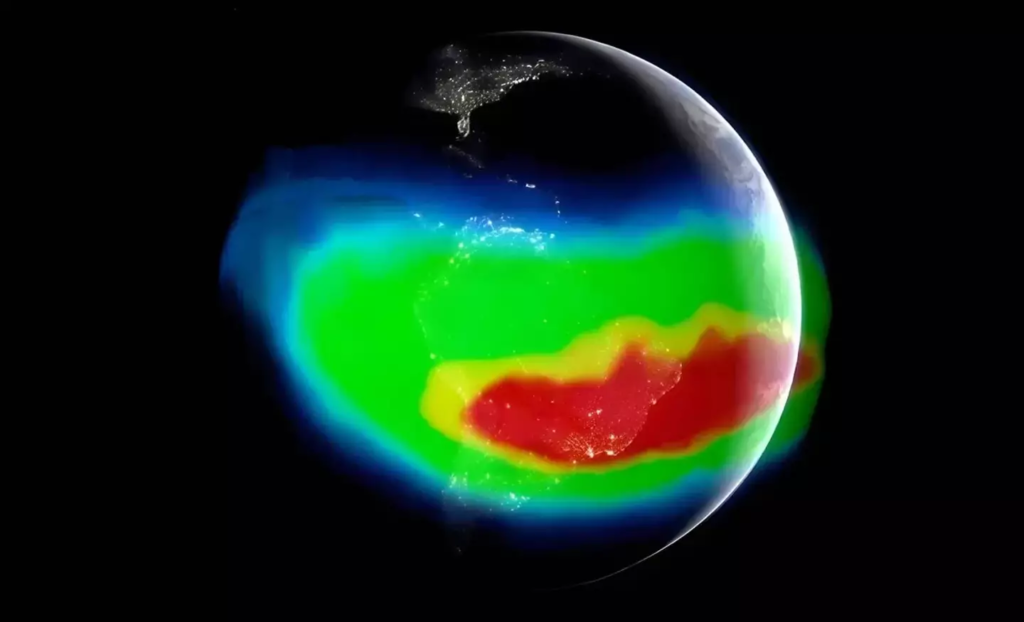
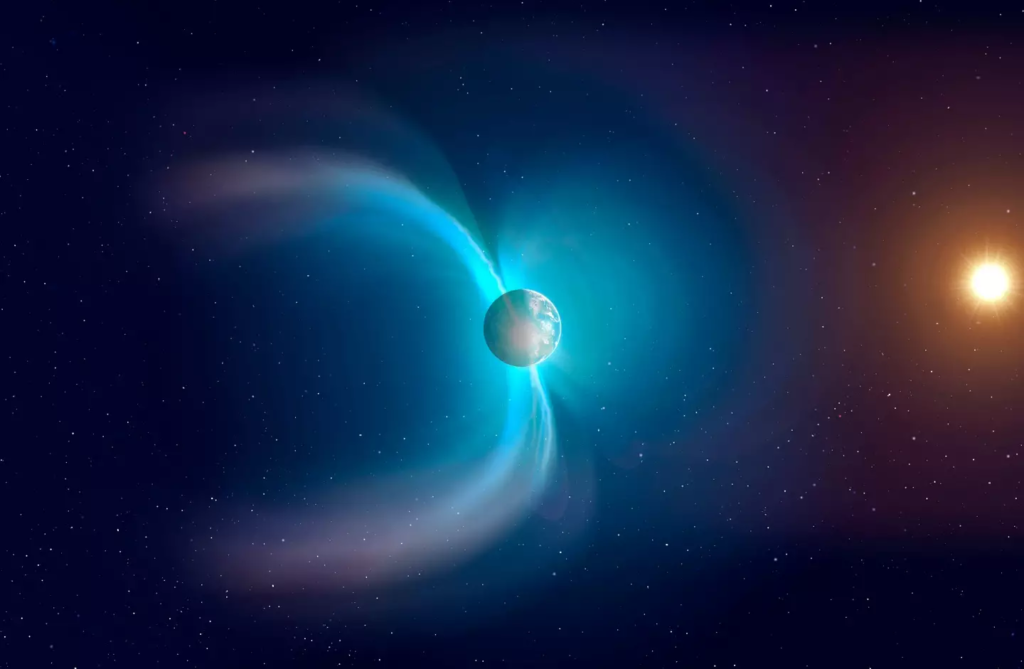
The South Atlantic Anomaly is essentially a “dent” in Earth’s magnetic field, creating an area where the magnetic shield is weaker than elsewhere on the planet. This dent spans a massive area, stretching from southwest Africa all the way across the South Atlantic Ocean, reaching parts of South America. Discovered in 1958, the SAA has since been closely monitored by NASA, which has raised concerns about its potential impacts.

To understand the significance of this anomaly, it’s important to know how Earth’s magnetic field works. The magnetic field acts like a protective bubble that shields our planet from harmful solar radiation, including charged particles from the Sun. Without this protection, life as we know it could not exist. The magnetic field prevents the Sun’s energy from directly reaching Earth, allowing biological processes to thrive.
However, in the region of the South Atlantic Anomaly, the magnetic field’s strength weakens significantly. This creates a unique problem: harmful solar radiation and high-energy particles can get closer to the Earth’s surface, where they can disrupt satellite technology and potentially impact life on Earth.
Why Should We Be Concerned About the SAA?
While the South Atlantic Anomaly doesn’t directly affect life on the planet’s surface just yet, its effects are already being felt by satellites and spacecrafts. The anomaly creates a high level of particle radiation that passes through this region of space, which can cause significant malfunctions in spacecraft and satellites. These high-energy particles can interfere with the electronic systems of satellites, leading to errors in data, signal loss, or complete malfunctions. Given how much modern life depends on satellite technology—think GPS, weather forecasting, communication networks, and medical support—these disruptions can have serious consequences.
NASA has emphasized that this region’s importance is not just about keeping satellites safe, but also understanding how changes in the SAA might be linked to shifts in the Earth’s atmosphere. Scientists are concerned that alterations in the SAA may indicate broader changes happening to the planet’s magnetic field or even the environment surrounding Earth.
Changing Patterns in the South Atlantic Anomaly
One of the more worrying aspects of the SAA is that it is not static. In fact, recent data collected in 2020 revealed that the anomaly is both expanding westward and weakening in intensity. The SAA has also started to split into two distinct lobes, a development that poses new challenges for satellite missions, especially as they pass through this weakened magnetic region.
NASA scientists continue to track the anomaly’s evolution as it could potentially impact the future of space exploration. As humanity looks toward missions to Mars and other distant planets, space agencies, including NASA and private companies like SpaceX, will need to account for the risks posed by the SAA. A malfunction in spacecraft systems due to the high-energy proton strikes could have catastrophic effects, such as loss of mission data or, in extreme cases, spacecraft damage.
A Potential Threat to Space Exploration
Space exploration is advancing rapidly, with missions to other planets becoming a reality. As missions venture further into space, the effects of the South Atlantic Anomaly could become a serious obstacle. High-energy proton strikes that occur within the SAA could cause irreparable damage to spacecraft electronics, putting entire missions in jeopardy. This is why, when spacecrafts enter the SAA, satellite operators are forced to temporarily shut down their equipment to protect it from these destructive particles.
For Earth-based technologies, the threat of radiation exposure from the SAA is also significant. Disruptions to satellite systems that support communication, weather monitoring, and other services could lead to widespread consequences. In a world increasingly reliant on satellite-based systems, any disruption in these services could potentially jeopardize the safety and stability of modern life.

What is NASA Doing About It?
NASA is taking steps to monitor and study the SAA closely. Terry Sabaka, a geophysicist at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, highlighted the importance of continued observation to understand the full scope of the anomaly. “Even though the SAA is slow-moving, it is going through some change in morphology, so it’s also important that we keep observing it by having continued missions,” Sabaka said. This ongoing research is crucial in developing predictive models to understand the potential impacts of the anomaly as it continues to evolve.
By monitoring the South Atlantic Anomaly, NASA can help create better models that will enable satellite operators to anticipate disruptions and minimize the damage caused by the anomaly. This is especially important as space agencies prepare for the future of space exploration and as Earth’s technological infrastructure becomes more dependent on satellite technology.
User Comments:
Sarah T.
“This is a fascinating look at how space weather impacts the technology we rely on! I never realized how much we depend on satellites until reading this article. I’m curious to learn more about how satellites are designed to handle the SAA. Check out this link about how NASA protects satellites from space radiation!”
John M.
“As someone who works in communications, I’m worried about the potential impacts of the SAA on satellite communications. What would happen if this problem gets worse? It’s something I think we should all be paying attention to. This article offers an interesting take on radiation shielding for satellites.”
Rachel F.
“I had no idea about the South Atlantic Anomaly until now! This is such a critical issue, especially as we look towards more space missions. I’m excited to see what NASA comes up with to protect our satellites in the future. If you’re curious about space weather and its effects, here’s a great guide on space weather from NASA!”
What’s at Stake for Humanity?
While Earth’s magnetic field may seem like an invisible force, it is one of the planet’s most essential protective mechanisms. The SAA’s existence highlights just how vulnerable our technology and infrastructure can be in the face of natural cosmic phenomena. As our reliance on satellite technology continues to grow, understanding the dynamics of the SAA and its long-term impacts will be critical.
NASA’s research into this anomaly is not just about protecting space technology, but also safeguarding the technologies and services we depend on every day. With space exploration expanding into uncharted territory, the SAA could present a major risk to the success of future missions.
As the magnetic field continues to shift and evolve, the implications of the South Atlantic Anomaly may continue to affect both space exploration and life on Earth. The continued study of this “dent” in the magnetic field is essential to understanding how our planet’s natural forces can influence humanity’s progress in the years to come.
Featured Image Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Getty Stock Image