BREAKING: Massive Iceberg A23A Breaks Free, Begins Drifting Across the Southern Ocean
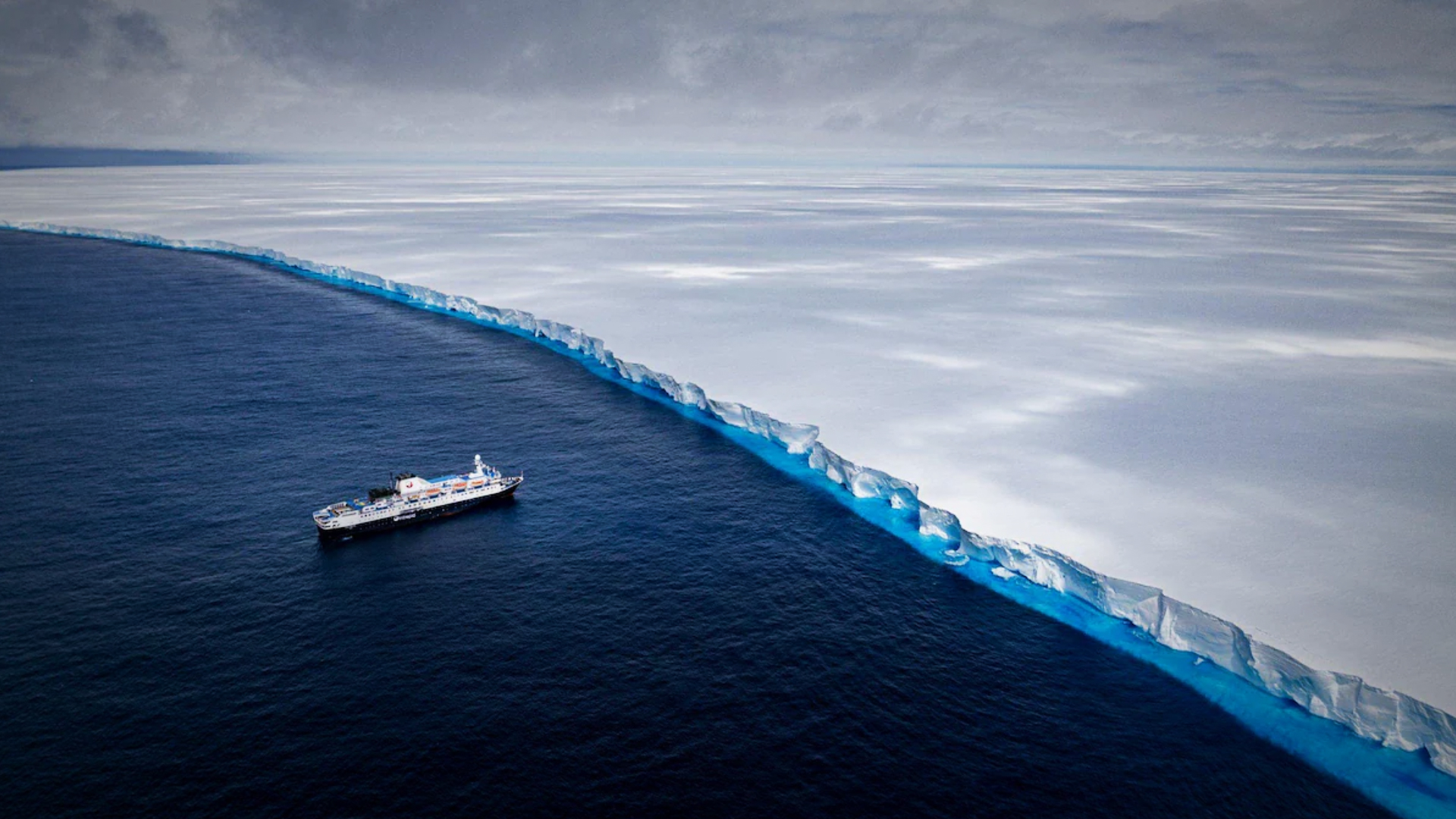

Iceberg A23A, one of the largest icebergs in the world, has broken free from its icy confines and is now drifting across the Southern Ocean. Covering an astonishing 1,418 square miles (4,000 square kilometers)—approximately three times the size of New York City—and weighing just under 1 trillion tons, this frozen colossus is capturing the attention of scientists worldwide.
CREDIT: USGS / LANDSAT
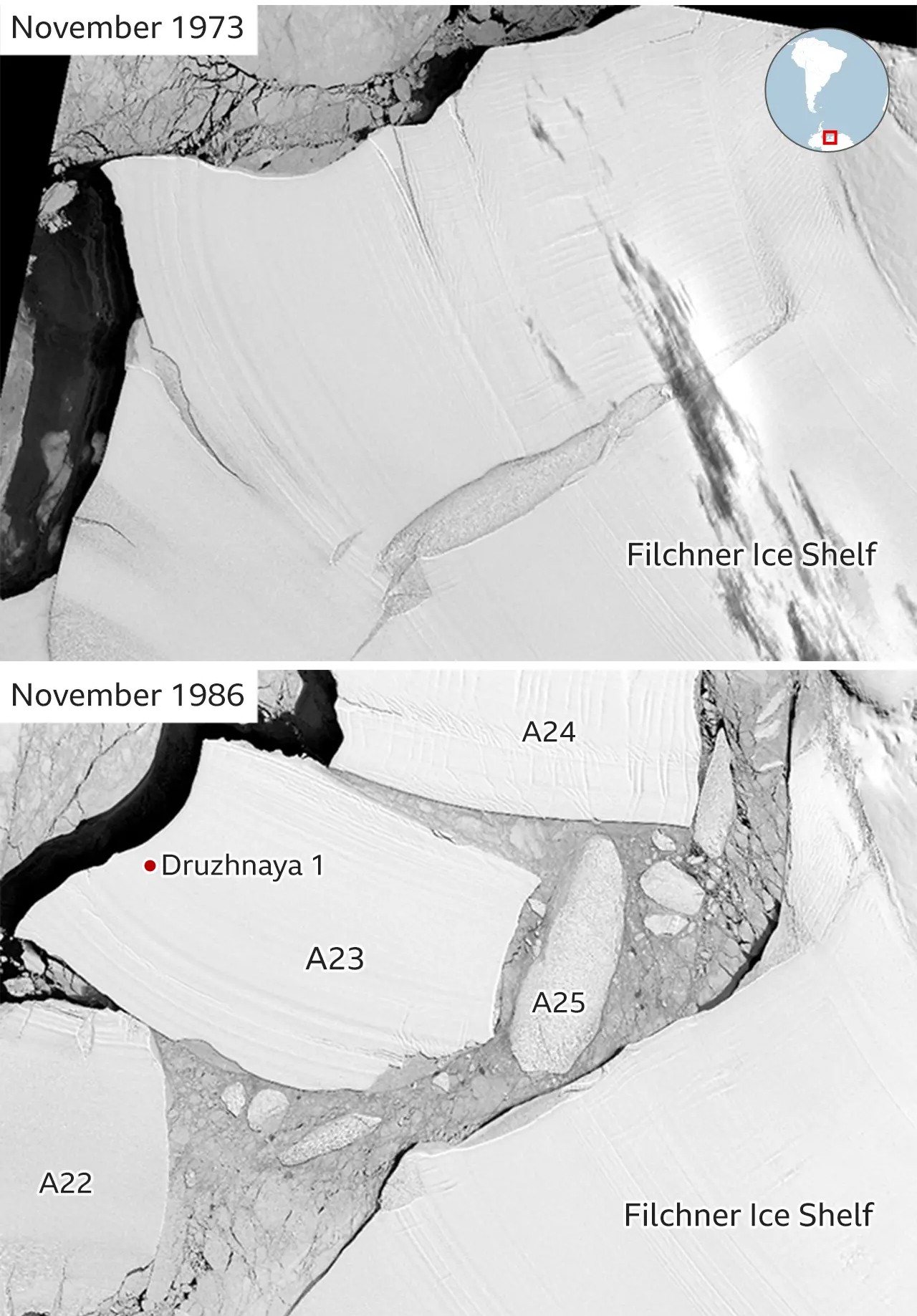
A 37-Year Journey
A23A originally calved from Antarctica’s Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf back in 1986, making headlines for its massive size. For over three decades, the iceberg remained grounded on the floor of the Weddell Sea, unable to move due to its sheer weight and size. However, in 2020, the iceberg began its slow journey toward the Southern Ocean.
Earlier this year, its progress was temporarily halted when it became trapped by a Taylor column—a swirling ocean current created by an underwater mountain. This natural phenomenon effectively pinned A23A in place, but recent events have seen the iceberg escape the current’s grip and resume its free-floating movement.

Tracking A23a's movements as it heads towards the Southern Ocean. (British Antarctic Survey/YouTube)
Drifting Toward “Iceberg Alley”
Scientists monitoring A23A predict that winds and ocean currents will steer the iceberg toward the Southern Ocean’s infamous “iceberg alley.” This region is a well-known pathway for large icebergs, funneling them toward warmer waters near South Georgia Island. Here, A23A is expected to encounter rising temperatures that will significantly accelerate its melting process.
@reuters A nature photographer captures the A23a iceberg, the world’s largest, during a trip on the Antarctic Ocean. #News #Reuters #A23a #iceberg #ocean #Antarctica
Environmental Implications of Melting
The melting of A23A carries both opportunities and challenges for the surrounding environment:
- Release of Nutrients: As A23A melts, it will release accumulated dust and debris collected over decades from the ocean floor. This process could enrich the water with nutrients like iron, which may stimulate phytoplankton growth. Phytoplankton plays a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere, potentially offsetting some greenhouse gas emissions.
- Ecosystem Impact: The release of nutrients could boost marine food chains, benefiting species that rely on phytoplankton, such as krill and fish. However, sudden changes in nutrient levels may also disrupt local ecosystems.
- Habitat Loss and Rising Sea Levels: Large icebergs like A23A serve as habitats for ice-dependent species such as penguins and seals. As the iceberg melts, these species may face habitat loss. Additionally, the melting of polar ice contributes to rising sea levels, threatening coastal regions worldwide
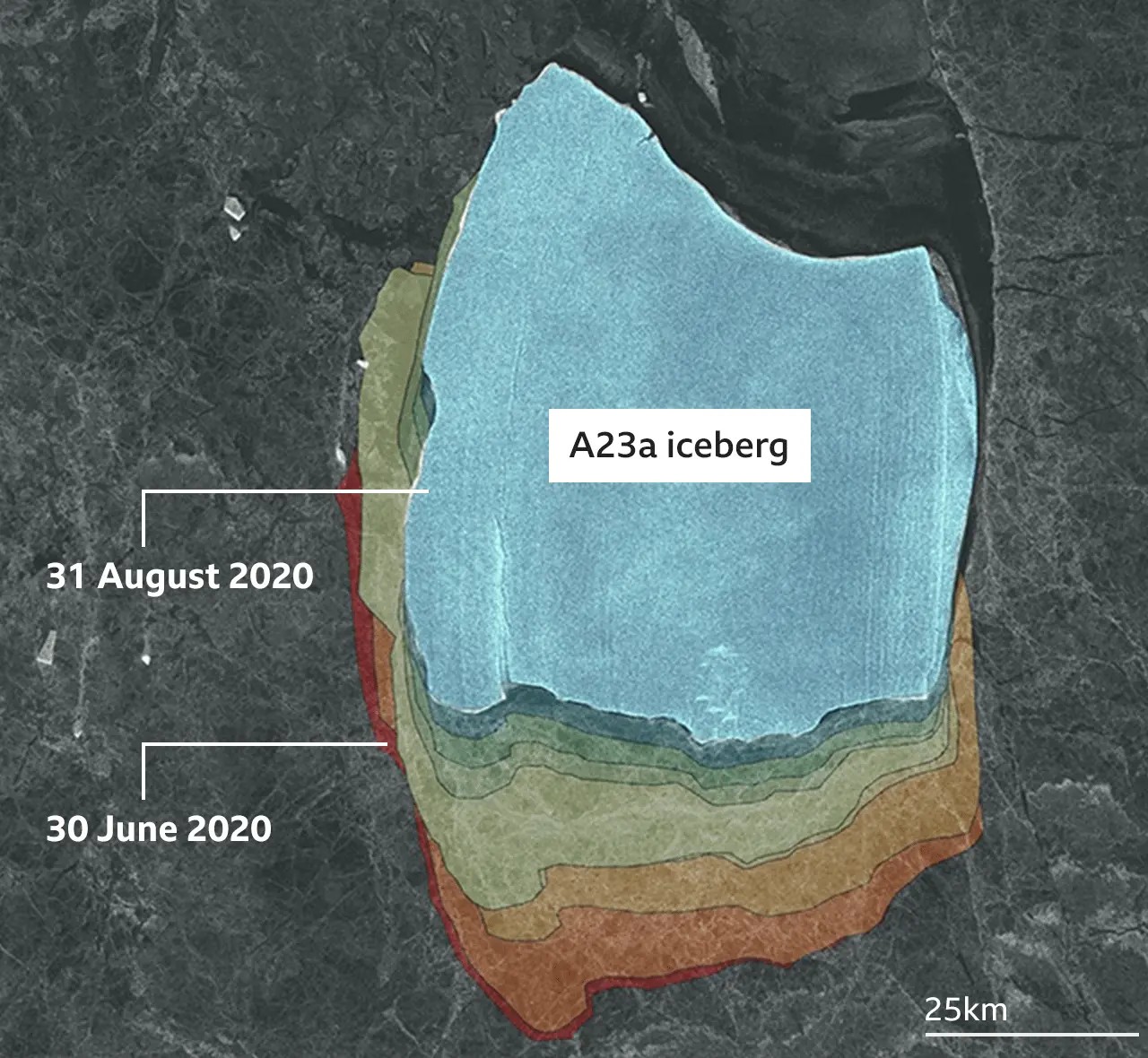
Source: Polar View / BBC
Concerns for the Future
The movement of A23A is part of a broader trend of increasing polar ice loss linked to climate change. Scientists are closely monitoring its journey not only to understand its immediate impact but also to gain insights into the long-term effects of melting icebergs on global ecosystems.
Other potential concerns include:
- Storm Activity: The introduction of large amounts of freshwater into the ocean could disrupt salinity levels, potentially intensifying ocean storms or altering weather patterns.
- Carbon Cycle Disruptions: While iron release may boost CO2 absorption through phytoplankton, it’s unclear how other elements released from the iceberg might affect the ocean’s carbon cycle.
A Scientific Watchlist
A23A’s journey provides a rare opportunity for researchers to study the lifecycle of massive icebergs and their interactions with marine ecosystems. Observations will be critical in understanding how melting icebergs contribute to global sea level rise, ocean nutrient dynamics, and the overall health of Earth’s climate systems.
As the iceberg drifts further into warmer waters, scientists and environmentalists will keep a close eye on its progress and its potential to reshape both marine environments and our understanding of climate impacts.
Stay tuned for updates on this colossal iceberg’s journey and its implications for the planet.
Featured image credit: Polar View / BBC, British Antarctic Survey/YouTube, USGS / LANDSAT






